Docker’s purpose is to build and manage compute images and to launch them in a container. So, the most useful commands do and expose this information.
Here’s a cheat sheet on the top Docker commands to know and use.
Build docker image $ cd /path/to/Dockerfile $ sudo docker build. View running processes $ sudo docker ps View all processes $ sudo docker ps -a Run an image in a new container daemonized $ sudo docker run -d Run an image in interactive mode with the command /bin/bash $ sudo docker run -i -t /bin/bash. Cheat Sheet: docker CLI & Dockerfile Table of Contents Introduction Container Architecture. $ docker run -name mywildfly -d -p 8080:8080 jboss/wildfly 3. Downloads an image from the Docker registry images List the images in the local repository run run -it -it Runs the image in interactive mode e.g. Use command bin/sh to open a Linux shell ps List the running containers and their status -a Adds containers that have are stopped rmi.
(This is part of our Docker Guide. Use the right-hand menu to navigate.)
Images and containers
The docker command line interface follows this pattern:
docker <COMMAND>

The docker images and container commands grant access to the images and containers. From here, you are permitted to do something with them, hence:
There are:
- is lists the resources.
- cp copies files/folders between the container and the local file system.
- create creates new container.
- diff inspects changes to files or directories in a running container.
- logs fetches the logs of a container.
- pause pauses all processes within one or more containers.
- rename renames a container.
- run runs a new command in a container.
- start starts one or more stopped containers.
- stop stops one or more running containers.
- stats displays a livestream of containers resource usage statistics.
- top displays the running processes of a container.
View resources with ls
From the container ls command, the container id can be accessed (first column).
Docker Run Cheat Sheet Pdf
Control timing with start, stop, restart, prune
- start starts one or more stopped containers.
- stop stops one or more running containers.
- restart restarts one or more containers.
- prune (the best one!) removes all stopped containers.
Name a container

View vital information: Inspect, stats, top
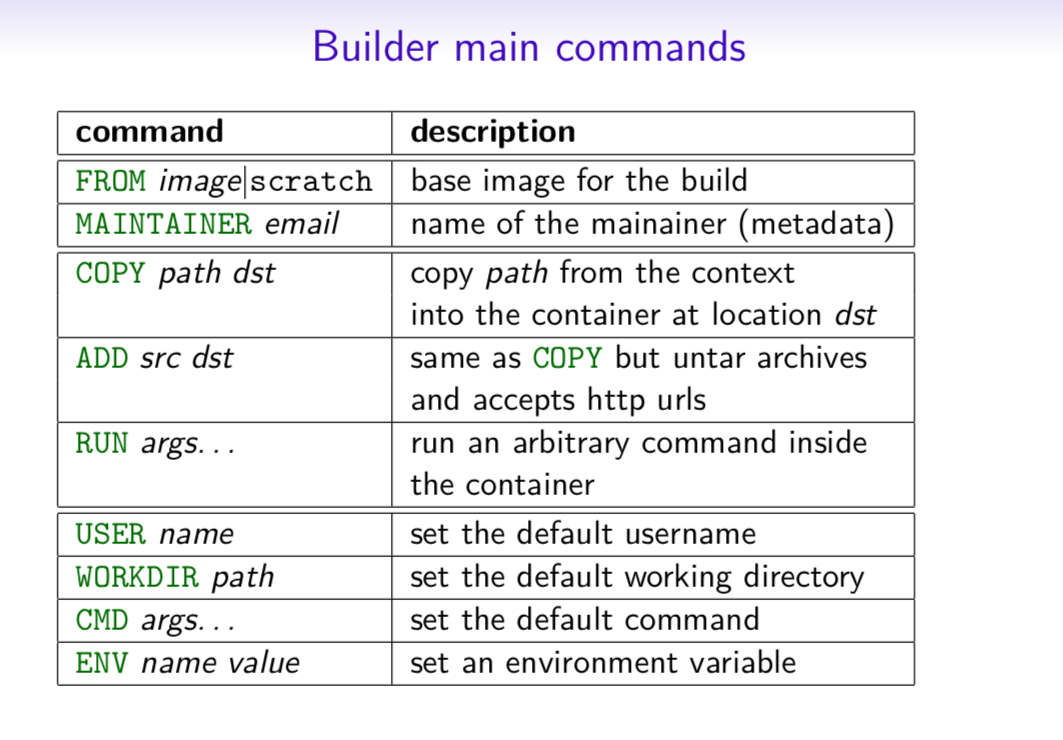
Docker Run Cheat Sheet Download
- stats displays a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics

- top displays the running processes of a container:
Docker Run Cheat Sheet
- inspect displays detailed information on one or more containers. With inspect, a JSON is returned detailing the name and states and more of a container.
Additional resources
Docker Run Cheat Sheet Printable
For more on this topic, there’s always the Docker documentation, the BMC DevOps Blog, and these articles:

Comments are closed.